The NASA Artemis rocket launch marks one of the most ambitious and historic chapters in modern space exploration. After more than five decades since the Apollo missions, NASA is preparing to send humans back to the Moon and eventually to Mars. The Artemis program is not just about revisiting the lunar surface; it is about building a sustainable human presence in deep space and testing technologies that will define the future of exploration.
In this detailed guide, we will explore the NASA Artemis rocket launch in depth, including its objectives, rockets, spacecraft, launch timeline, missions, challenges, and what it means for humanity. Whether you are a space enthusiast, student, researcher, or general reader, this article will give you a complete understanding of the Artemis program.
What Is the NASA Artemis Program?
The NASA Artemis program is a long-term human spaceflight initiative designed to return astronauts to the Moon and establish a permanent lunar presence. The program is named after Artemis, the twin sister of Apollo in Greek mythology, symbolizing a new era following the Apollo Moon missions.
The central goal of the Artemis program is to conduct regular Moon missions that will enable scientific discovery, technological innovation, and international collaboration. The NASA Artemis rocket launch is the backbone of this initiative, carrying astronauts, spacecraft, and cargo beyond Earth’s orbit.
Unlike Apollo, Artemis focuses on sustainability. Instead of short visits, NASA plans to build lunar infrastructure such as the Lunar Gateway space station and surface habitats that will support long-duration missions.
Why the NASA Artemis Rocket Launch Is So Important
The importance of the NASA Artemis rocket launch goes far beyond symbolic value. It represents a shift in how space exploration is approached in the 21st century.
First, the Artemis missions aim to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon. This reflects NASA’s commitment to diversity and inclusion in space exploration.
Second, Artemis will test advanced systems required for deep-space travel, including life support, radiation protection, and autonomous navigation.
Third, the Moon will serve as a testing ground for future missions to Mars. By mastering operations on the Moon, NASA can reduce the risks associated with long-distance human missions.
In short, the NASA Artemis rocket launch is a stepping stone toward humanity becoming a multi-planetary species.
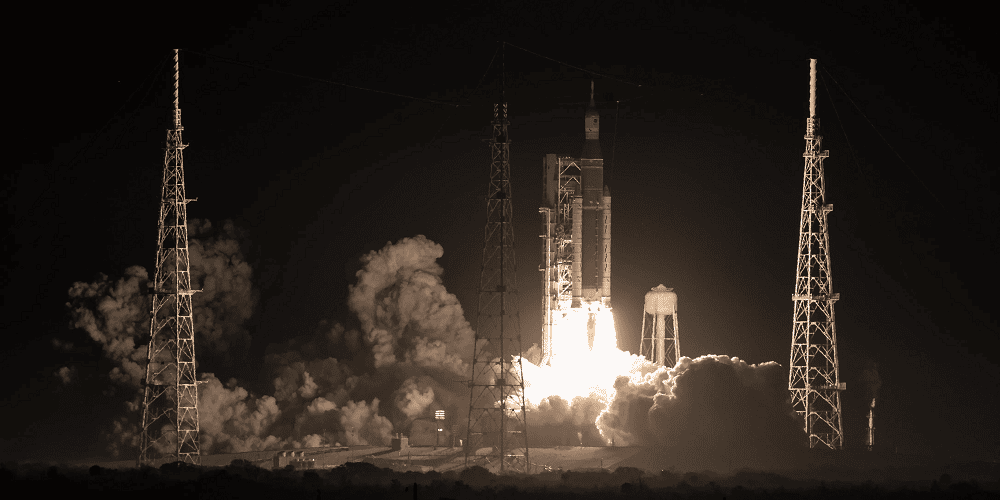
The Rocket Behind the NASA Artemis Rocket Launch: Space Launch System (SLS)
At the heart of every NASA Artemis rocket launch is the Space Launch System, commonly known as SLS. It is the most powerful rocket NASA has ever built.
The SLS is designed to carry astronauts and heavy payloads beyond low Earth orbit. Its power surpasses that of the Saturn V rocket used during the Apollo era.
The rocket consists of a massive core stage powered by four RS-25 engines, two solid rocket boosters, and an upper stage that propels the spacecraft toward the Moon. Together, these components generate millions of pounds of thrust during liftoff.
The Space Launch System is not a single-use design. It will evolve over time with more powerful versions that can support deeper space missions, including future Mars expeditions.
Orion Spacecraft and Its Role in the NASA Artemis Rocket Launch
The Orion spacecraft is the crew capsule used in the NASA Artemis rocket launch. Built to carry astronauts farther than any human-rated spacecraft before, Orion is designed for deep-space travel.
Orion can support a crew of up to four astronauts for missions lasting several weeks. It includes advanced life support systems, navigation technology, and heat shields capable of withstanding extreme temperatures during atmospheric re-entry.
During the NASA Artemis rocket launch, Orion sits atop the Space Launch System and separates once it reaches space. From there, it travels toward the Moon, enters lunar orbit, and later returns astronauts safely to Earth.
Orion is a critical element in ensuring the safety and success of Artemis missions.
Timeline of NASA Artemis Rocket Launch Missions
The Artemis program is divided into multiple missions, each building upon the previous one. The NASA Artemis rocket launch schedule reflects a step-by-step approach to lunar exploration.
Artemis I was an uncrewed test mission designed to validate the SLS rocket and Orion spacecraft. This mission proved that the systems could safely travel to the Moon and back.
Artemis II will be the first crewed NASA Artemis rocket launch. Astronauts will orbit the Moon but will not land on the surface. This mission will test life support and human operations in deep space.
Artemis III is expected to mark humanity’s return to the lunar surface. Astronauts will land near the Moon’s south pole, an area rich in water ice and scientific potential.
Future Artemis missions will focus on building lunar infrastructure and preparing for Mars missions.
NASA Artemis Rocket Launch and the Lunar South Pole
One of the most exciting aspects of the NASA Artemis rocket launch is its focus on the Moon’s south pole. Unlike the equatorial landing sites of Apollo, the south pole offers unique advantages.
This region contains permanently shadowed craters that may hold frozen water. Water is essential not only for drinking but also for producing oxygen and rocket fuel.
By landing near the south pole, Artemis missions can explore new scientific territory and test technologies for resource utilization. This approach supports NASA’s goal of sustainable exploration.
The NASA Artemis rocket launch is therefore not just about landing on the Moon, but about learning how to live and work there.
International Partnerships in the Artemis Program
The NASA Artemis rocket launch is a global effort involving international space agencies and commercial partners. Countries including Canada, Japan, and members of the European Space Agency are contributing technology, astronauts, and expertise.
One key component of international collaboration is the Lunar Gateway, a space station that will orbit the Moon. Gateway will serve as a staging point for lunar landings and deep-space missions.
Commercial companies are also playing a major role. NASA has partnered with private firms to develop lunar landers, cargo systems, and support services.
This collaborative model ensures that the NASA Artemis rocket launch benefits from global innovation and shared responsibility.
Challenges Facing the NASA Artemis Rocket Launch
Despite its promise, the NASA Artemis rocket launch faces significant challenges. Developing new technology at this scale is complex and costly.
Technical delays, budget constraints, and testing requirements have impacted mission timelines. The Space Launch System and Orion spacecraft have undergone extensive testing to ensure safety and reliability.
Another challenge is maintaining long-term political and financial support. Artemis is a multi-decade program that requires sustained commitment from governments and partners.
However, NASA continues to address these challenges through rigorous testing, transparency, and collaboration.
How the NASA Artemis Rocket Launch Differs from Apollo
While Artemis draws inspiration from Apollo, the two programs differ significantly in scope and vision.
Apollo missions were short-term and focused on achieving a single goal: landing humans on the Moon. In contrast, the NASA Artemis rocket launch supports long-term exploration and infrastructure development.
Artemis uses advanced digital systems, automation, and reusable technologies that were not available during Apollo.
Another key difference is inclusivity. Artemis aims to land the first woman and a diverse group of astronauts on the Moon, reflecting modern values and global participation.
NASA Artemis Rocket Launch and Future Mars Missions
One of the most important reasons behind the NASA Artemis rocket launch is preparation for Mars. The Moon serves as an ideal testing ground due to its proximity to Earth.
Technologies tested during Artemis missions will inform future Mars spacecraft design, surface habitats, and mission planning.
By learning how to operate in deep space, manage long-duration missions, and use local resources, NASA reduces the risks of sending humans to Mars.
In this way, the NASA Artemis rocket launch is a bridge between Earth, the Moon, and the Red Planet.
Scientific Goals of the NASA Artemis Rocket Launch
Science is a major driver of the Artemis program. Each NASA Artemis rocket launch carries instruments and experiments designed to answer fundamental questions about the Moon and the solar system.
Scientists will study lunar geology, search for water ice, and analyze the Moon’s history. These findings can provide insight into how Earth and other planets formed.
Artemis missions will also test new scientific tools and methods that can be applied to future exploration.
The data collected will benefit researchers worldwide and expand our understanding of space.
Public Interest and Inspiration from the NASA Artemis Rocket Launch
The NASA Artemis rocket launch has captured public imagination around the world. It represents hope, curiosity, and human achievement.
NASA actively engages students, educators, and space enthusiasts through live broadcasts, educational programs, and outreach initiatives.
By inspiring the next generation of scientists and engineers, the Artemis program ensures that space exploration remains a shared human endeavor.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the NASA Artemis rocket launch?
The NASA Artemis rocket launch refers to missions under the Artemis program that use the Space Launch System rocket to send the Orion spacecraft and astronauts toward the Moon.
Why is NASA returning to the Moon with Artemis?
NASA is returning to the Moon to establish a sustainable human presence, conduct scientific research, and prepare for future missions to Mars.
Which rocket is used in the NASA Artemis rocket launch?
The Space Launch System (SLS) is the rocket used for all NASA Artemis rocket launch missions.
What spacecraft carries astronauts during Artemis missions?
Astronauts travel in the Orion spacecraft, which is designed for deep-space missions beyond Earth’s orbit.
Will Artemis land humans on the Moon?
Yes, future Artemis missions will land astronauts on the Moon, starting with Artemis III.
Where will Artemis astronauts land on the Moon?
Artemis astronauts are expected to land near the Moon’s south pole, an area with potential water ice deposits.
How is Artemis different from Apollo?
Artemis focuses on long-term exploration, international collaboration, advanced technology, and sustainability, unlike the short-term Apollo missions.
Is the NASA Artemis rocket launch part of a Mars plan?
Yes, Artemis is a critical step toward future human missions to Mars by testing deep-space technologies and operations.
Who are NASA’s partners in the Artemis program?
NASA partners include international space agencies and private companies that contribute technology, landers, and expertise.
How many Artemis missions are planned?
NASA plans multiple Artemis missions over the coming decades, with each mission building toward sustained lunar exploration.
Conclusion
The NASA Artemis rocket launch is more than a space mission. It is a bold vision for the future of human exploration. By returning to the Moon with modern technology, international cooperation, and a focus on sustainability, NASA is laying the groundwork for humanity’s next giant leap.
From powerful rockets and advanced spacecraft to scientific discovery and global inspiration, the Artemis program represents a turning point in space history. As each NASA Artemis rocket launch unfolds, it brings us closer to a future where humans explore not just the Moon, but the broader solar system.


.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)

.jpg)
.jpg)

.jpg)
.jpg)


.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)


Leave A Comment
0 Comment