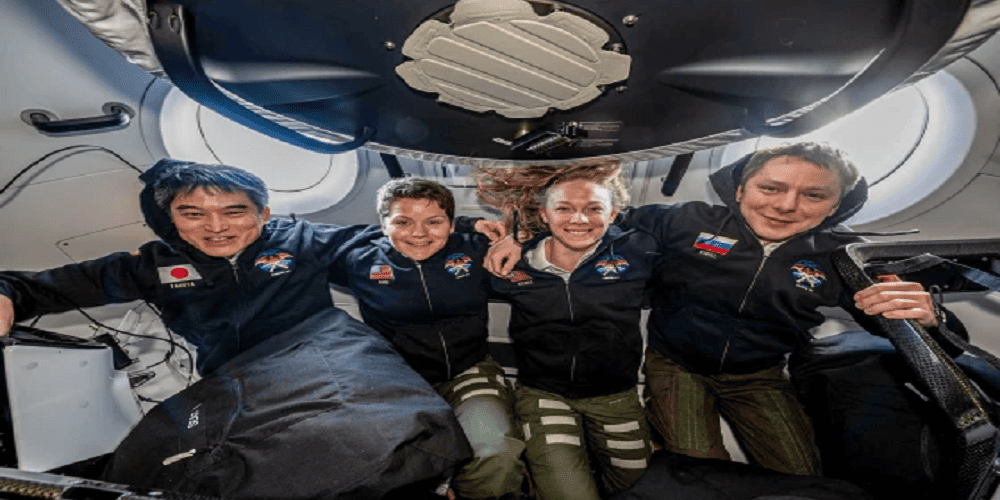
The phrase NASA astronauts return captures one of the most critical and emotional moments in space exploration. After months—or sometimes nearly a year—aboard the International Space Station (ISS), the safe return of astronauts to Earth marks the successful completion of complex missions that push human knowledge, technology, and endurance. Every NASA astronauts return mission reflects years of preparation, cutting-edge engineering, and international cooperation.
In recent years, the concept of NASA astronauts return has gained global attention due to advances in commercial spacecraft, long-duration spaceflight, and renewed plans for Moon and Mars missions. From launch to landing, the return journey is just as dangerous and technically demanding as traveling into space.
This article explores the full meaning of NASA astronauts return missions, how they work, why they matter, recent developments, challenges faced during reentry, and what the future holds for human spaceflight.
Understanding the Importance of NASA Astronauts Return
When people think about space missions, the launch often steals the spotlight. However, NASA astronauts return is arguably the most dangerous phase of any space mission. Reentering Earth’s atmosphere at speeds exceeding 17,000 miles per hour requires absolute precision.
A successful NASA astronauts return signifies:
- Mission objectives have been completed
- Astronauts have survived long-duration microgravity
- Spacecraft systems performed flawlessly
- Scientific data and samples have been safely delivered
Each NASA astronauts return adds to NASA’s growing body of knowledge, helping engineers improve spacecraft design, life-support systems, and emergency protocols.
How NASA Astronauts Return to Earth
The process of NASA astronauts return is highly structured and carefully monitored. Astronauts do not simply “fall back” to Earth. Instead, the return journey follows a precise sequence of events.
Departure from the International Space Station
Before NASA astronauts return, they:
- Transfer mission data and experiment samples
- Conduct handover briefings with incoming crews
- Secure personal and mission equipment
- Enter the return spacecraft, such as SpaceX Crew Dragon or previously the Soyuz capsule
Once undocked, the spacecraft slowly backs away from the ISS, beginning the journey home.
Deorbit Burn and Atmospheric Reentry
A crucial step in NASA astronauts return is the deorbit burn. This controlled engine firing slows the spacecraft enough to allow Earth’s gravity to pull it into the atmosphere.
During reentry:
- Temperatures can exceed 3,500 degrees Fahrenheit
- A heat shield protects the capsule
- Communication blackout may occur due to plasma formation
This phase is often described as the most intense part of NASA astronauts return missions.
Parachute Deployment and Splashdown or Landing
As the spacecraft slows:
- Parachutes deploy to reduce speed
- Capsules either splash down in the ocean or land on solid ground
- Recovery teams quickly secure the spacecraft
Once hatches are opened, NASA astronauts return to fresh air and gravity for the first time in months.
Physical Effects After NASA Astronauts Return
Returning to Earth is not easy on the human body. After extended time in microgravity, astronauts experience significant physical challenges during NASA astronauts return.
Common effects include:
- Muscle weakness
- Bone density loss
- Balance and coordination issues
- Fluid shifts causing dizziness
NASA medical teams assist astronauts immediately after landing. Recovery can take weeks or even months, depending on mission duration. Studying these effects helps NASA prepare for longer missions, making each NASA astronauts return scientifically valuable.
Recent NASA Astronauts Return Missions
In recent years, NASA astronauts return missions have become more frequent due to partnerships with private space companies. SpaceX’s Crew Dragon spacecraft has played a major role in modern NASA astronauts return operations.
These missions demonstrate:
- Increased launch and return flexibility
- Reduced reliance on foreign spacecraft
- Enhanced safety and automation
Each successful NASA astronauts return strengthens confidence in commercial spaceflight systems and paves the way for future exploration.
Role of SpaceX in NASA Astronauts Return
One of the most transformative developments in recent space history is the role of SpaceX. With Crew Dragon, NASA astronauts return to Earth aboard a reusable, American-built spacecraft.
Key advantages include:
- Automated docking and undocking
- Precision splashdown capabilities
- Faster post-landing recovery
- Cost efficiency
The success of these missions has redefined how NASA astronauts return, setting new standards for safety and innovation.
Challenges Faced During NASA Astronauts Return
Despite advanced technology, NASA astronauts return missions are never routine. Numerous risks must be managed carefully.
Technical Challenges
- Heat shield integrity
- Parachute deployment timing
- Navigation accuracy
Environmental Risks
- Weather conditions at landing zones
- Ocean currents during splashdown
- Atmospheric disturbances
Human Factors
- Fatigue after long missions
- Disorientation due to gravity readjustment
NASA’s meticulous planning and constant monitoring reduce risks, but the complexity of NASA astronauts return cannot be underestimated.
Why NASA Astronauts Return Missions Matter to Earth
The benefits of NASA astronauts return missions extend far beyond space exploration. Research conducted aboard the ISS and brought back to Earth has applications in medicine, technology, and environmental science.
Examples include:
- Advancements in osteoporosis treatment
- Improved water purification systems
- Innovations in materials science
- Better understanding of climate change
Every NASA astronauts return brings valuable insights that improve life on Earth.
Psychological Aspects of NASA Astronauts Return
Returning home after months in space is emotionally intense. Astronauts often describe NASA astronauts return as a mixture of relief, joy, and sensory overload.
Adjustments include:
- Relearning simple movements
- Coping with crowded environments
- Reconnecting with family and society
NASA provides psychological support before and after NASA astronauts return to ensure long-term well-being.
NASA Astronauts Return and International Cooperation
The ISS is a global partnership involving multiple space agencies. Many NASA astronauts return missions involve coordination with international partners.
This cooperation:
- Enhances safety through shared expertise
- Strengthens diplomatic relationships
- Promotes peaceful use of outer space
NASA astronauts return missions symbolize what humanity can achieve through collaboration rather than competition.
Training for NASA Astronauts Return
Astronauts train extensively for their return long before launch. Simulations prepare them for every possible scenario during NASA astronauts return.
Training includes:
- Emergency landing drills
- Survival training for ocean and land recovery
- Medical response simulations
- Spacecraft system operations
This rigorous preparation ensures astronauts can respond effectively during the most critical moments of NASA astronauts return.
The Role of Recovery Teams After NASA Astronauts Return
Once astronauts land, recovery teams swing into action. These teams are essential to a successful NASA astronauts return.
Their responsibilities include:
- Securing the spacecraft
- Conducting initial medical evaluations
- Transporting astronauts to recovery facilities
- Retrieving scientific payloads
The smooth coordination between NASA, the military, and private partners ensures a safe conclusion to NASA astronauts return missions.
How NASA Astronauts Return Missions Shape Future Space Travel
Every NASA astronauts return mission influences future exploration strategies. Lessons learned are applied to upcoming missions under programs like Artemis and planned Mars expeditions.
Key areas of impact:
- Long-duration life-support systems
- Radiation exposure management
- Crew health monitoring
- Spacecraft reusability
Understanding NASA astronauts return is crucial for achieving sustainable human presence beyond Earth.
NASA Astronauts Return and the Artemis Program
The Artemis program aims to return humans to the Moon and eventually reach Mars. Safe and reliable NASA astronauts return systems are central to these goals.
Unlike ISS missions:
- Lunar returns involve higher reentry speeds
- Spacecraft must endure greater thermal stress
- Recovery logistics are more complex
Advancements gained from current NASA astronauts return missions directly support Artemis mission planning.
Public Interest and Media Coverage of NASA Astronauts Return
NASA astronauts return missions capture global attention. Live broadcasts, social media updates, and press conferences bring space exploration into millions of homes.
This visibility:
- Inspires future scientists and engineers
- Increases public support for space programs
- Educates people about science and technology
The excitement surrounding NASA astronauts return reinforces the importance of space exploration in modern society.
Technological Innovations Driven by NASA Astronauts Return
Developing safe return systems has led to innovations that benefit many industries.
Technologies influenced by NASA astronauts return include:
- Heat-resistant materials
- Advanced navigation software
- Medical monitoring devices
- Emergency response systems
These advancements demonstrate how space challenges drive technological progress on Earth.
Environmental Considerations of NASA Astronauts Return
NASA continually works to minimize the environmental impact of space missions. Modern NASA astronauts return systems aim to be more sustainable.
Efforts include:
- Reusable spacecraft
- Reduced debris during reentry
- Careful selection of landing zones
Responsible planning ensures NASA astronauts return missions align with environmental stewardship.
Future of NASA Astronauts Return Missions
As space exploration evolves, NASA astronauts return missions will become more advanced and frequent. Future spacecraft may feature:
- Improved automation
- Enhanced crew comfort
- Faster recovery times
- Greater reusability
With plans for deep-space missions, understanding and improving NASA astronauts return processes will remain a top priority.
Common Myths About NASA Astronauts Return
Many misconceptions exist about how astronauts come back to Earth.
Some myths include:
- Astronauts free-fall uncontrollably to Earth
- Reentry is fully automated without human oversight
- Recovery is instant and effortless
In reality, NASA astronauts return is a carefully controlled, highly monitored, and physically demanding process.
Conclusion: The Significance of NASA Astronauts Return
The journey does not end when astronauts complete their mission in orbit. NASA astronauts return is the final, crucial chapter of every spaceflight. It represents the success of years of training, engineering excellence, and international cooperation.
Each safe NASA astronauts return advances science, improves technology, and brings humanity one step closer to becoming a multi-planetary species. As NASA continues to explore deeper into space, the importance of reliable and safe return missions will only grow.
FAQs on NASA Astronauts Return
What does NASA astronauts return mean?
NASA astronauts return refers to the process of astronauts safely traveling back to Earth after completing their mission in space, usually from the International Space Station.
How long does NASA astronauts return take?
From undocking to landing, NASA astronauts return typically takes several hours, depending on orbital position and landing conditions.
Is NASA astronauts return dangerous?
Yes, it is one of the most risky phases of a space mission due to high reentry speeds, extreme heat, and precise timing requirements.
What spacecraft are used for NASA astronauts return?
Currently, NASA astronauts return primarily uses SpaceX Crew Dragon spacecraft, with future vehicles planned under the Artemis program.
How do astronauts feel after NASA astronauts return?
Astronauts often experience weakness, dizziness, and balance issues after NASA astronauts return due to readjusting to Earth’s gravity.
Why is NASA astronauts return important for future missions?
Studying NASA astronauts return helps NASA improve spacecraft safety, astronaut health, and mission planning for Moon and Mars exploration.
Do astronauts need medical care after NASA astronauts return?
Yes, astronauts receive immediate medical evaluation and ongoing care to help them recover from long-duration spaceflight effects.


.jpg)
.png)

.jpg)
.jpg)











Leave A Comment
0 Comment