In today’s dynamic financial market, stocks graphs play a pivotal role for investors, traders, and financial analysts alike. Whether you are a seasoned trader or a beginner looking to enter the stock market, understanding how to read and interpret a stocks graph is essential. Stocks graphs, also known as stock charts, visually represent the performance of a stock over a specific period. They provide insights into price trends, trading volume, and market sentiment, helping investors make informed decisions.
What is a Stocks Graph?
A stocks graph is a visual representation of the historical and current performance of a stock. It shows the price movement of a stock over a given timeframe, ranging from minutes to years. Stocks graphs typically include the following key elements:
- Price: This represents the value of the stock at a specific point in time.
- Timeframe: The duration over which the stock price is tracked, such as daily, weekly, monthly, or yearly intervals.
- Volume: The number of shares traded within a specific period, often represented as bars at the bottom of the graph.
- Trends: Upward, downward, or sideways trends indicate the market sentiment and potential price direction.
By analyzing a stocks graph, investors can detect patterns, make predictions, and implement strategies that align with their investment goals.
Types of Stocks Graphs
There are several types of stocks graphs, each serving a unique purpose. The most common types include:
1. Line Graph
A line graph is the simplest form of stock chart. It connects the closing prices of a stock over a selected timeframe, providing a clear picture of the overall trend. Line graphs are useful for beginners because they are easy to interpret and highlight the general direction of a stock’s price movement.
2. Bar Chart
A bar chart provides more detailed information than a line graph. Each bar represents the stock’s opening, closing, highest, and lowest prices during a specific period. Bar charts help investors understand price volatility and market activity.
3. Candlestick Chart
A candlestick chart is widely used by professional traders due to its detailed representation of price movement. Each candlestick shows the opening, closing, high, and low prices. The color of the candlestick indicates whether the stock closed higher or lower than it opened. Candlestick charts are excellent for identifying patterns and trends that can signal potential market movements.
How to Read a Stocks Graph
Understanding a stocks graph requires familiarity with certain basic principles:
1. Identifying Trends
Trends are the backbone of stock analysis. An uptrend occurs when prices consistently rise, a downtrend happens when prices fall, and a sideways trend shows minimal price movement. Recognizing these trends helps investors decide whether to buy, sell, or hold a stock.
2. Support and Resistance Levels
Support levels are price points where a stock tends to stop falling due to increased buying interest. Conversely, resistance levels are price points where a stock struggles to rise due to selling pressure. These levels are crucial for predicting price movements and setting entry or exit points.
3. Volume Analysis
Analyzing trading volume alongside price movement provides insight into the strength of a trend. High volume during an uptrend indicates strong buying interest, while low volume during a downtrend suggests weak selling pressure. Volume analysis helps validate the significance of price changes.
4. Moving Averages
Moving averages smooth out price data to identify the overall direction of a stock. Common types include the simple moving average (SMA) and exponential moving average (EMA). Moving averages can indicate potential buy or sell signals when a stock’s price crosses above or below the average line.
Importance of Stocks Graphs
Stocks graphs are not just for traders; they are valuable for anyone investing in the stock market. Here are some reasons why they are important:
- Informed Decision-Making: By analyzing trends, support, resistance, and volume, investors can make strategic decisions rather than relying on guesswork.
- Risk Management: Stocks graphs help investors set stop-loss orders and manage risk by identifying critical price points.
- Predict Market Behavior: Historical patterns often repeat themselves. Studying stocks graphs enables investors to anticipate potential market movements.
- Compare Performance: Investors can compare multiple stocks to identify better investment opportunities based on historical performance.
Common Patterns in Stocks Graphs
Certain patterns in stocks graphs often indicate potential price movements. Some common patterns include:
- Head and Shoulders: Suggests a reversal in trend; usually indicates a bearish trend if formed at the top.
- Double Top and Double Bottom: Indicates strong resistance or support levels and potential reversals.
- Triangles: Ascending, descending, or symmetrical triangles signal continuation or reversal trends.
- Cup and Handle: A bullish pattern that predicts upward price movement.
Recognizing these patterns requires practice, but mastering them can significantly improve trading strategies.
Using Technology to Analyze Stocks Graphs
Modern technology has made stock analysis more accessible than ever. Platforms like TradingView, Yahoo Finance, and Google Finance offer interactive stocks graphs with advanced tools for technical analysis. Investors can customize charts, apply indicators, and study historical trends with ease.
Tips for Beginners
For those new to stock investing, here are some practical tips:
- Start with line graphs to understand the overall trend.
- Gradually explore candlestick and bar charts to gain deeper insights.
- Focus on long-term trends rather than short-term fluctuations to avoid unnecessary stress.
- Combine technical analysis with fundamental analysis for a comprehensive understanding.
- Always set stop-loss orders to minimize potential losses.
Conclusion
A stocks graph is more than just a visual tool—it is a roadmap for investors and traders. By understanding how to read and interpret these graphs, individuals can make informed investment decisions, manage risks effectively, and potentially maximize returns. Whether you are analyzing short-term trends or long-term performance, mastering stocks graphs is a vital step toward becoming a successful investor.
FAQs About Stocks Graph
Q1: What is the difference between a line graph and a candlestick chart?
A line graph is simple and shows only the closing prices over time, making it easy for beginners to spot trends. A candlestick chart provides detailed information, including opening, closing, high, and low prices, and is better for analyzing market patterns and predicting price movements.
Q2: How can I use a stocks graph to decide when to buy or sell a stock?
By identifying trends, support and resistance levels, and analyzing trading volume, investors can determine optimal entry and exit points. For example, buying near a support level during an uptrend or selling near a resistance level in a downtrend can improve decision-making.
Q3: Are stocks graphs useful for long-term investors?
Yes, long-term investors can use stocks graphs to study historical performance, identify consistent growth trends, and avoid buying during temporary market dips. Combining stock charts with fundamental analysis helps in making strategic long-term investments.

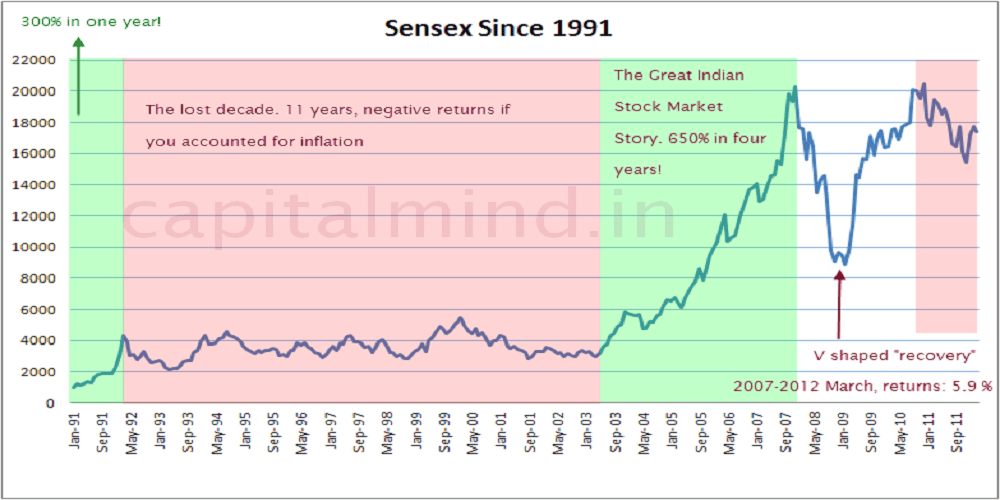

.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)

.jpg)
.jpg)

.jpg)
.jpg)


.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)


Leave A Comment
0 Comment