Gold has fascinated humanity for centuries, not only as a symbol of wealth and beauty but also as a powerful financial asset. In modern times, the gold price plays a crucial role in global markets, influencing investment decisions, central bank policies, and consumer behavior. Whether you are a seasoned investor or someone simply curious about precious metals, understanding how the gold price works can help you make smarter financial choices.
This detailed guide explores the history, drivers, trends, and future outlook of the gold price, along with practical insights for investors.
Understanding Gold as an Asset
Gold is more than just a shiny metal used in jewelry. It is considered a safe-haven asset, meaning investors often turn to it during times of economic uncertainty. The gold price tends to move differently from stocks and bonds, which makes it valuable for diversification.
Unlike paper currency, gold cannot be printed or created at will. Its limited supply and universal acceptance contribute to the long-term strength of the gold price. Central banks, governments, and private investors all hold gold as part of their reserves.
Historical Perspective of Gold Price
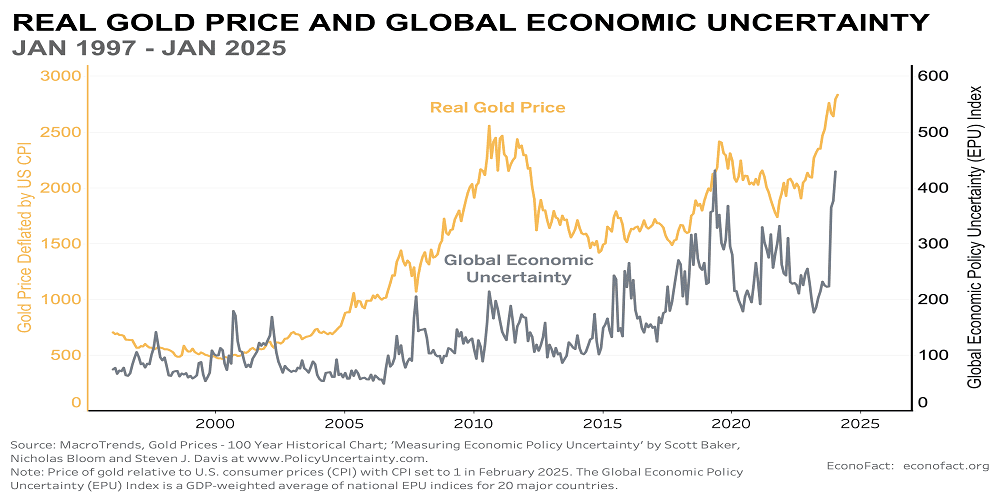
Looking at history helps explain why the gold price remains so important. For centuries, gold was directly linked to currencies through the gold standard. Although most countries abandoned this system in the 20th century, the gold price still reflects global confidence in paper money.
During major financial crises, such as the 2008 global recession and periods of high inflation, the gold price has typically surged. Investors seek stability when markets are volatile, and gold often benefits from that shift in sentiment.
Over the decades, the gold price has experienced both sharp rises and corrections, but the overall long-term trend has shown resilience.
Key Factors That Influence Gold Price
Several economic and geopolitical forces shape the movement of the gold price. Understanding these factors can help investors anticipate potential trends.
1. Inflation
One of the biggest drivers of the gold price is inflation. When the cost of goods and services rises, the value of paper money falls. Gold is often seen as a hedge against inflation, which can push the gold price higher during inflationary periods.
2. Interest Rates
Interest rates have an inverse relationship with the gold price. When rates are low, gold becomes more attractive because it does not pay interest, yet it holds value. Higher interest rates, on the other hand, can reduce demand and put pressure on the gold price.
3. Currency Strength
The gold price is usually quoted in U.S. dollars. When the dollar weakens, gold becomes cheaper for international buyers, which can drive the gold price upward. A strong dollar may have the opposite effect.
4. Geopolitical Tensions
Wars, political instability, and global conflicts often increase uncertainty in financial markets. During such times, the gold price typically rises as investors look for safety.
5. Central Bank Policies
Central banks hold large gold reserves. When they buy gold, it can support the gold price. When they sell, it may create downward pressure. Their monetary policies also indirectly affect the gold price through interest rates and inflation.
6. Supply and Mining
Gold mining production affects supply levels. If mining output slows while demand stays strong, the gold price can rise. Discoveries of new gold reserves may influence the long-term outlook but rarely cause sudden changes.
Gold Price and Global Economy
The gold price often reflects the overall health of the global economy. During periods of strong growth and stable markets, investors may prefer riskier assets like stocks, which can limit gains in the gold price.
However, during recessions or market crashes, the gold price often strengthens. This is because gold is viewed as a store of value when confidence in financial systems declines.
Emerging markets also play a major role. Countries like India and China have high demand for gold jewelry and investment products, which significantly impacts the gold price.
Investment Options Linked to Gold Price
Investors have several ways to gain exposure to the gold price. Each method has its own advantages and risks.
Physical Gold
Buying physical gold in the form of coins, bars, or jewelry is the most traditional method. The value of these items is closely linked to the gold price, though additional costs like storage and insurance must be considered.
Gold ETFs
Exchange-traded funds (ETFs) allow investors to track the gold price without owning physical metal. These funds are traded on stock exchanges and offer liquidity and convenience.
Gold Mining Stocks
Shares of gold mining companies are indirectly tied to the gold price. When the gold price rises, mining companies may become more profitable, potentially increasing their stock value. However, company-specific risks also apply.
Gold Futures and Options
These are advanced financial instruments used by traders to speculate on future movements in the gold price. They offer high potential returns but also carry significant risk.
Gold Price vs Other Precious Metals
While silver, platinum, and palladium are also valuable, the gold price is often more stable. Gold has a unique combination of industrial, decorative, and investment demand.
Silver prices can be more volatile due to heavy industrial use. Platinum and palladium are influenced strongly by automotive demand. In contrast, the gold price is more directly tied to macroeconomic factors and investor sentiment.
Seasonal Trends in Gold Price
Interestingly, the gold price can show seasonal patterns. Demand often rises during wedding seasons and festivals in countries like India, which can push the gold price higher during certain months.
Investment demand may also increase at year-end or during times of market uncertainty, adding further seasonal influence on the gold price.
Gold Price and Inflation Hedge
One of the main reasons people invest in gold is to protect their wealth from inflation. Historically, when inflation rises sharply, the gold price has tended to increase as well.
However, this relationship is not always immediate. Short-term movements in the gold price can be influenced by many other factors, but over the long run, gold has maintained purchasing power better than many currencies.
Role of Technology and Digital Gold
Modern technology has made investing in gold easier than ever. Digital platforms now allow investors to buy and sell gold linked to the current gold price without handling physical metal.
Digital gold, gold-backed cryptocurrencies, and online trading apps have increased accessibility, especially among younger investors. These innovations have made tracking and investing based on the gold price more convenient.
Risks Associated with Gold Price Investments
Although gold is considered safe, investing based on the gold price still involves risks.
- Price Volatility: The gold price can fluctuate significantly in the short term.
- No Passive Income: Gold does not pay dividends or interest.
- Storage Costs: Physical gold requires secure storage.
- Market Timing: Buying when the gold price is at a peak may limit returns.
Understanding these risks helps investors make balanced decisions.
Gold Price Forecast and Future Outlook
Predicting the gold price is challenging because many variables are involved. However, certain trends can offer clues.
If global inflation remains high, central banks continue to buy gold, and geopolitical tensions persist, the gold price may remain strong. On the other hand, stable economic growth and rising interest rates could slow its momentum.
In the long term, limited supply and consistent global demand are likely to support the gold price, making it a relevant asset for future generations.
How to Track Gold Price
Investors can monitor the gold price through financial news websites, commodity exchanges, and trading platforms. Prices are typically quoted per ounce in U.S. dollars but may also be available in local currencies.
Real-time tracking helps investors decide when to buy or sell based on movements in the gold price.
Tips for Investing Based on Gold Price
- Diversify: Do not rely solely on gold; use it as part of a broader portfolio.
- Think Long Term: The gold price can be volatile short term but stable long term.
- Avoid Emotional Decisions: Market panic can push the gold price up or down quickly.
- Understand Costs: Consider fees, taxes, and storage when investing.
Cultural and Emotional Value of Gold
Beyond finance, gold holds deep cultural significance in many societies. Weddings, religious events, and celebrations often involve gold purchases. This cultural demand helps maintain long-term support for the gold price.
Environmental and Ethical Considerations
Gold mining can have environmental impacts. As awareness grows, ethical sourcing and sustainable mining practices are becoming more important. These factors may influence supply and indirectly affect the gold price in the future.
Conclusion
The gold price remains one of the most closely watched indicators in global finance. Driven by inflation, interest rates, currency movements, and geopolitical events, gold continues to serve as a store of value and a portfolio diversifier.
Whether you choose physical gold, ETFs, or mining stocks, understanding the forces behind the gold price can help you make informed investment decisions. While no asset is risk-free, gold’s long history and universal appeal make it a unique and enduring part of the financial world.
FAQs About Gold Price
1. What determines the gold price daily?
The gold price is influenced by global demand and supply, currency strength, interest rates, inflation expectations, and geopolitical events.
2. Why does the gold price rise during crises?
Investors see gold as a safe asset. During economic or political crises, demand increases, which can push the gold price higher.
3. Is gold a good investment for the long term?
Gold can be a good long-term hedge against inflation and currency risk, and the gold price has historically shown resilience over time.
4. How can beginners invest in gold linked to the gold price?
Beginners can start with gold ETFs or digital gold platforms that track the gold price without requiring physical storage.
5. Does the gold price always go up when inflation rises?
Not always immediately, but over time, high inflation often supports a higher gold price.
6. Why is the gold price quoted in U.S. dollars?
Gold is traded globally, and the U.S. dollar is the primary international trading currency, which standardizes the gold price worldwide.
7. Can the gold price fall significantly?
Yes, the gold price can decline due to rising interest rates, a strong dollar, or reduced demand, especially in the short term.
8. What is the difference between gold rate and gold price?
Both terms are often used interchangeably. The gold price usually refers to the international market value, while the gold rate may include local taxes and dealer premiums.
9. How often does the gold price change?
The gold price changes constantly during market hours due to real-time trading in global commodity markets.
10. Is physical gold better than paper gold?
It depends on investor preference. Physical gold offers direct ownership, while paper gold tracks the gold price with greater convenience and liquidity.


.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)

.jpg)
.jpg)

.jpg)
.jpg)


.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)


Leave A Comment
0 Comment