
Grow your savings with zero risk
Fixed Deposit
Fixed Deposit (FD): A fixed deposit (FD), also known as a term deposit or time deposit, is a financial instrument offered by banks and financial institutions. It allows individuals to deposit a lump sum of money for a predetermined period at a fixed interest rate, which is higher than the interest rate offered on regular savings accounts. Fixed deposits are considered a safe and low-risk investment option.
Fixed deposits have a predetermined maturity period, which can range from a few months to several years. The depositor agrees to keep the funds locked in for the specified tenure. These deposits offer a fixed rate of interest for the entire tenure, which is determined at the time of opening the FD and remains unchanged throughout the deposit period, providing certainty of returns.
One of the key features of fixed deposits is their low risk. They are considered low-risk investments as they are backed by the issuing bank or financial institution. The principal amount invested in the FD is generally protected, and depositors are assured of receiving the predetermined interest income at maturity.
Depositors can choose the amount they wish to invest in a fixed deposit, subject to the minimum deposit requirement set by the bank or financial institution. Higher deposit amounts may qualify for preferential interest rates. Upon maturity, fixed deposits may be automatically renewed for a similar tenure at prevailing interest rates unless the depositor specifies otherwise. This ensures continuity of investment and interest income.
Fixed deposits offer a stable and predictable source of income for investors seeking safety and liquidity. However, they may have limitations such as penalties for premature withdrawal and fixed returns that may not keep pace with inflation over the long term.
What are the types of fixed deposit?
Types of Fixed Deposits:
- Regular Fixed Deposits: Regular fixed deposits are the most common type, where individuals deposit a lump sum of money for a fixed period at a fixed interest rate. The interest rate remains constant throughout the tenure of the deposit, providing stability and predictability of returns.
- Senior Citizen Fixed Deposits: Senior citizen fixed deposits are specifically designed for individuals above a certain age (typically 60 years or older). These deposits often offer higher interest rates compared to regular fixed deposits to provide additional income for senior citizens during retirement.
- Tax-Saving Fixed Deposits: Tax-saving fixed deposits, also known as tax-saving FDs, allow individuals to invest a certain amount of money for a fixed tenure (usually five years) and claim tax benefits under Section 80C of the Income Tax Act, 1961. The investment amount up to a specified limit qualifies for deduction from taxable income.
- Cumulative Fixed Deposits: Cumulative fixed deposits accumulate interest over the deposit period and pay out the principal amount along with accumulated interest at maturity. The interest is compounded quarterly or annually, providing higher returns compared to regular fixed deposits.
- Non-Cumulative Fixed Deposits: Non-cumulative fixed deposits pay out the interest earned at regular intervals, such as monthly, quarterly, half-yearly, or annually, depending on the depositor's preference. The principal amount remains intact and is returned to the depositor at maturity.
- Flexi Fixed Deposits: Flexi fixed deposits offer flexibility in terms of deposit and withdrawal of funds during the deposit period. Depositors can withdraw funds partially or fully before maturity without incurring penalties, subject to certain terms and conditions specified by the bank or financial institution.
- Corporate Fixed Deposits: Corporate fixed deposits are offered by corporate entities, including non-banking financial companies (NBFCs) and corporate institutions, to raise funds from investors. These deposits may offer higher interest rates compared to bank fixed deposits but involve higher risk.
Each type of fixed deposit has its own features, benefits, and risks, and individuals should choose the type that best suits their investment goals, risk tolerance, and financial needs.

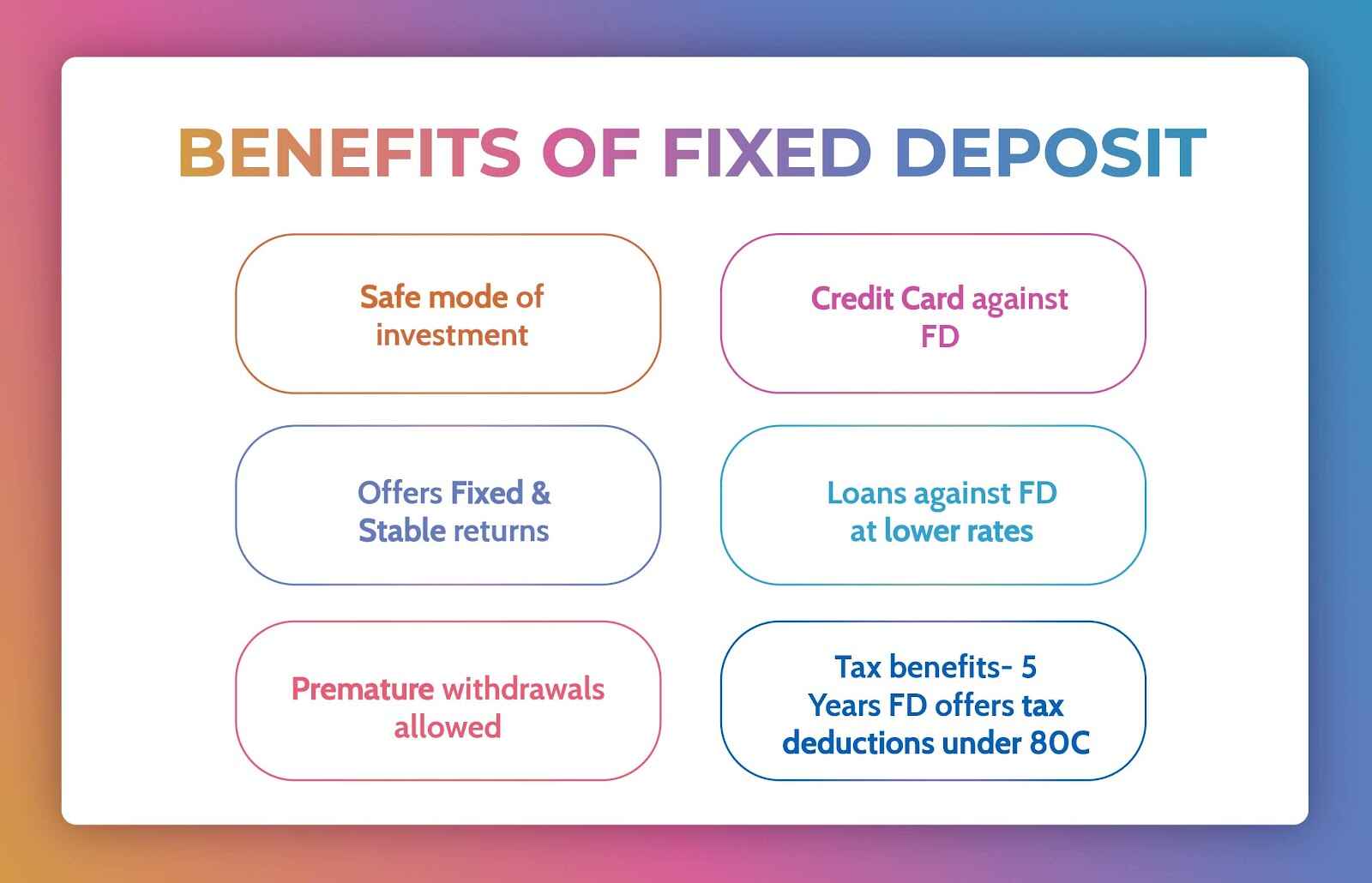
What are the features and benefits of fixed deposit?
Features and Benefits of Fixed Deposits:
- Stability: Fixed deposits offer stable and predictable returns as they provide a fixed rate of interest for the entire tenure of the deposit. This makes them an attractive option for conservative investors seeking safety and certainty of returns.
- Low Risk: Fixed deposits are considered low-risk investments as they are backed by the issuing bank or financial institution. The principal amount invested in the FD is generally protected, and depositors are assured of receiving the predetermined interest income at maturity.
- Flexibility: Fixed deposits offer flexibility in terms of deposit amount, tenure, and interest payout frequency. Depositors can choose the amount they wish to invest, select the tenure that suits their investment horizon, and opt for interest payouts at regular intervals or at maturity.
- Higher Returns: Fixed deposits typically offer higher interest rates compared to savings accounts, providing investors with the opportunity to earn higher returns on their savings. The interest rates may vary depending on factors such as deposit amount, tenure, and prevailing market conditions.
- Tax Benefits: Tax-saving fixed deposits allow individuals to claim tax benefits under Section 80C of the Income Tax Act, 1961, by investing in fixed deposits for a specified tenure (usually five years). The investment amount up to a specified limit qualifies for deduction from taxable income.
- Automatic Renewal: Upon maturity, fixed deposits may be automatically renewed for a similar tenure at prevailing interest rates unless the depositor specifies otherwise. This ensures continuity of investment and interest income without the need for manual intervention.
- Senior Citizen Benefits: Senior citizen fixed deposits offer higher interest rates to individuals above a certain age (typically 60 years or older), providing additional income for retirees and elderly investors.
Fixed deposits provide a secure and convenient way for individuals to grow their savings while preserving capital and earning a steady stream of income. They are suitable for investors seeking stability, safety, and liquidity for their funds.
How does a fd works?
How Does a Fixed Deposit (FD) Work?
A fixed deposit (FD) works by allowing individuals to deposit a lump sum of money with a bank or financial institution for a predetermined period, known as the tenure, at a fixed rate of interest. The depositor agrees to keep the funds locked in for the specified tenure, during which the deposited amount earns interest at the agreed-upon rate. Here's how the process of opening and operating an FD typically works:
- Opening an FD: To open an FD, the depositor needs to visit a bank or financial institution and fill out an application form. The form requires details such as the deposit amount, tenure, interest payout frequency, and nominee information. The depositor may need to provide identification documents such as a PAN card, Aadhaar card, passport, or driving license for KYC (Know Your Customer) verification.
- Choosing the Tenure and Amount: The depositor selects the tenure and deposit amount based on their investment goals, risk tolerance, and liquidity requirements. Longer tenures typically offer higher interest rates, while larger deposit amounts may qualify for preferential interest rates.
- Agreeing to Terms: The depositor agrees to the terms and conditions of the FD, including the fixed interest rate, tenure, and any penalties for premature withdrawal. Once the application is processed and approved, the FD is opened, and the deposit amount is credited to the depositor's account.
- Earning Interest: Throughout the tenure of the FD, the deposited amount earns interest at the fixed rate agreed upon at the time of opening the FD. The interest may be compounded quarterly, semi-annually, or annually, depending on the bank's policies and depositor's preference.
- Interest Payout: At the end of the tenure, the depositor receives the maturity amount, which includes the principal amount along with accumulated interest. The interest can be paid out at regular intervals (in the case of non-cumulative FDs) or compounded and paid out at maturity (in the case of cumulative FDs).
- Renewal or Withdrawal: Upon maturity, the depositor has the option to renew the FD for another tenure at prevailing interest rates or withdraw the maturity amount. If the depositor chooses to withdraw the amount before maturity, they may incur penalties or forfeit a portion of the interest earned, depending on the bank's policies.
Overall, fixed deposits provide a secure and convenient way for individuals to grow their savings while earning a steady stream of income. They are suitable for investors seeking stability, safety, and liquidity for their funds.

Who is eligible for fd?
Eligibility for Fixed Deposit (FD):
Fixed deposits (FDs) are typically available to a wide range of individuals, including:
- Resident Individuals: Resident individuals, both salaried and self-employed, are eligible to open fixed deposits with banks or financial institutions. They can open FDs in their own name or jointly with another individual.
- Minors: Minors, under the guardianship of their parents or legal guardians, can also invest in fixed deposits. The FD can be opened in the name of the minor, with the parent or guardian acting as the signatory.
- Senior Citizens: Senior citizens, typically aged 60 years or older, are eligible for special FD schemes offered by banks with higher interest rates. These schemes are designed to provide additional income for retirees and elderly investors.
- Hindu Undivided Families (HUFs): HUFs, which consist of members of a family bound together by bloodline and commonality of property, can also invest in fixed deposits.
- Trusts, Partnerships, and Corporates: Trusts, partnerships, companies, and other corporate entities are eligible to open fixed deposits for investment purposes. They may have separate procedures and documentation requirements for opening FD accounts.
It's important to note that eligibility criteria may vary depending on the bank or financial institution's policies and regulations governing fixed deposits. Additionally, individuals may need to fulfill KYC (Know Your Customer) requirements and provide identification documents such as PAN card, Aadhaar card, passport, or driving license to open an FD account.
What are the taxation on fd earnings?

Taxation on Fixed Deposit (FD) Earnings:
The interest earned on fixed deposits (FDs) is subject to taxation as per the income tax laws of the country. In India, the interest earned on FDs is treated as income and is taxable under the Income Tax Act, 1961. Here are the key points regarding taxation on FD earnings:
- TDS (Tax Deducted at Source): Banks and financial institutions are required to deduct Tax Deducted at Source (TDS) on the interest earned on FDs if the interest income exceeds a certain threshold. The current threshold for TDS on FD interest is ₹40,000 for individuals below 60 years of age and ₹50,000 for senior citizens aged 60 years and above.
- Income Tax Slabs: The interest income earned on FDs is added to the individual's total income for the financial year and taxed as per the applicable income tax slab rates. The income tax slabs determine the rate at which the interest income is taxed based on the individual's total income.
- Taxation for Senior Citizens: Senior citizens (individuals aged 60 years and above) may avail of higher exemption limits on FD interest income. They can claim tax benefits under Section 80TTB of the Income Tax Act, which allows for a deduction of up to ₹50,000 on interest income earned from deposits with banks, post offices, and cooperative banks.
- Tax-Saving FDs: Tax-saving fixed deposits, also known as tax-saving FDs, offer tax benefits under Section 80C of the Income Tax Act. The investment amount in tax-saving FDs up to ₹1.5 lakh in a financial year qualifies for deduction from taxable income, reducing the tax liability of the investor.
- Taxation on Premature Withdrawal: In the case of premature withdrawal of FDs before the completion of the lock-in period, the interest earned may be subject to penalty and taxation at the individual's applicable income tax slab rates.
It's important for investors to understand the taxation implications of FD earnings and plan their investments accordingly. Consulting with a tax advisor or financial planner can help individuals optimize their tax liabilities and maximize their returns from fixed deposits.
What are the Documents required for FD?
Documents Required for Fixed Deposit (FD):
Opening a fixed deposit (FD) typically requires minimal documentation, but certain documents are necessary to comply with Know Your Customer (KYC) regulations and verify the depositor's identity and address. Here are the commonly required documents:
- Identity Proof: Valid government-issued identification documents such as Aadhaar card, PAN card, passport, voter ID card, or driver's license are required to verify the depositor's identity. These documents contain personal details such as name, photograph, and unique identification number.
- Address Proof: Documents that serve as proof of address are necessary to verify the residential address of the depositor. Accepted address proof documents include Aadhaar card, passport, utility bills (electricity, water, gas), bank statements, rent agreement, or any government-issued document containing the residential address.
- Photographs: Recent passport-size photographs of the depositor may be required for identification purposes and record-keeping by the bank or financial institution.
- PAN Card: The Permanent Account Number (PAN) card is mandatory for individuals opening fixed deposits exceeding ₹50,000 in a financial year. It is used for tax reporting and compliance purposes and helps track high-value transactions.
- Other KYC Documents: Additional KYC documents may be required as per the bank's policies and regulatory requirements. These may include declaration forms, nominee details, signature specimens, and any other documents deemed necessary by the bank or financial institution.
It's important for depositors to provide accurate and up-to-date documentation to comply with KYC norms and ensure smooth processing of their FD applications. Banks and financial institutions may have specific requirements, so individuals should inquire about the documents needed before opening an FD.